How To Set Up A Successful eLearning Production Process (Five-Phase Guide)
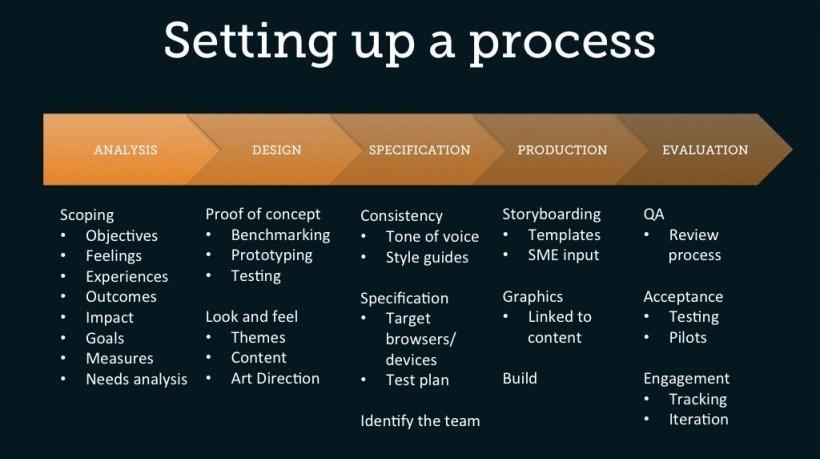
Let’s break down the five phases in the eLearning production process: Analysis, design, specification, production, and evaluation.
1. Analysis: Success starts with a plan and scope.

The analysis phase is all about setting up the project for success. Here you need to get the right people involved from the start: Lead author, project owner, and other stakeholders (management, graphic designers and Subject Matter Experts).
Next, you define a scope. Understand the design challenge that you’re about to address. For example, is it going to be a tool, survey, game, resource, course, micro-experience, simulation, diagnostic, reflection, or an app?
It’s important to remember that several factors can affect the scope: Budget, time, resources, and requirements.
If you gather your requirements thoroughly and arrive at an agreed goal before starting, you should find that you don’t get the dreaded scope creep during the production phase.
Once your scope is complete, you can search for any source content or materials that are available and can be reused. Schedule time with your stakeholders and Subject Matter Experts to analyze the content. Use that time to align the content against the goals and objectives to decide what to include or exclude.
Related: How to approach the analysis phase in the eLearning production process
2. Design: Test ideas before they are built.

The design phase involves benchmarking, prototyping, and testing. During this phase, you want to test your ideas before you build them. The goal is to prove that your ideas and concepts will work so you don’t waste time and money.
- Benchmarking defines where the project is headed and helps you to set the success criteria against which you will later evaluate. It’s key to make sure the project targets the learner, and is in line with your business values. It can also provide you with guidelines to determine how you deliver future eLearning courses.
- Prototyping involves testing concepts quickly so you can discard what is not viable in your context. The point is to get a visualization of potential solutions without actually making something that you’ll find difficult to throw out later.
- User testing during the design phase is specifically about testing your design against the end user. Think who your course is aimed at and how they will use it to solve a problem or fill a gap in their skills or knowledge.
Related: How to approach the design phase of the eLearning production process
3. Specification: Define what the end product looks like.

The specification phase is an important step that helps you focus on creating learning experiences that are tailored to your specific learner. The specification phase defines what the solution will look like and lists the quality assurance acceptance criteria against which the eLearning will later be tested. This can help when you come to evaluate a project.
- Consistency starts with creating a set of principles by which your team is going to abide. You don’t want to lock it down so much that you eliminate creativity, but you do need to provide support structures that enable team members to understand what it is you’re trying to achieve. Most learning professionals will create a guide as to what tools, style, and branding to use.
- Functionality helps you lock down exactly how your course will function. There are seven key areas to consider: platform and browser, reporting, media, navigation, accessibility, user interface/creative direction, and acceptance criteria.
- Identifying the right team involves deciding who will analyze the source content, build, proofread, manage the project, do the art direction, sign off deliverables, test, and integrate with the LMS. If you are working on a large project, allocate roles within your team.
Related: How to approach the specification phase in the eLearning production process
4. Production: Bring everything together and build.

The production phase is the point at which your planning and design come together. In this phase, you will need to map out content, create screens and templates, and involve graphic designers.
- Map out the overall experience using a mind map or flowchart (Coggle is the mind map I like to use). For example, let’s say you have 10 core interactions. Map out what will go into each of those interactions. Think about the discussion point, objective, and the experience that’s going to fall into each component.
- Storyboarding is the method of orchestrating all the elements that will make up the eLearning to create a score. This is much like in musical composition, where all team members can follow along using the same «notes». A storyboard explains how all the elements fit together. Here are 10 storyboarding elements you should include: text, graphics, animation, video, audio, resources, links, references, interactions, and activities.
- Create screens and templates from the list of the interaction and screen types you have jotted down. Tools like Elucidat come with a range of interaction and screen types already fully built and tested.
- Involve graphic designers right from the early stages of the project. They should be contributing throughout the eLearning process; helping to create graphics that support what the text is communicating.
Now it’s time to bring all the elements together – a little like an assembly line. The production phase becomes really simple if you’ve completed the work in the previous three stages (analysis, design, and specification). If you haven’t done the upfront work, you can easily waste a lot of time tinkering around and feeling lost.
Related: How to approach the production phase in the eLearning production process
5. Evaluation: Test the product meets the original specification.

The evaluation phase involves testing the project against the original specification. Use quality assurance (QA) testing, acceptance testing, and analysis to see how the product is performing in a range of the technical environments.
- Quality assurance (QA) testing can involve any of the following:
- Multi device testing.
Use Browser Stack to test in different environments, but if the project needs to run on a touch screen device, you should test it on the actual device. - Multi browser testing.
Browser Stack can help you to quickly test your course on different operating systems and browsers (learn more in this article by Elucidat). - Stress testing.
Try to break your eLearning. This lets you see how your course performs beyond the specified number of concurrent users. - Localization.
Test different languages to ensure they have been translated correctly.
- Multi device testing.
- Acceptance testing is done to determine if the course meets the requirements originally set out in the specification. Here you need to go back to your specification and test against all the aspects listed. This is really about making sure the course has the integrity to support a valid learning experience, and that it works in the real world.
- Engagement analytics can provide valuable information about how people are using your course and how you can improve it. Tools, like Google Analytics, give very detailed stats about how your course is performing. Use Google Analytics to analyze the following metrics:
- How long is someone spending on a page?
- Are some pages more popular than others?
- How long does your course really take to complete?
Related: How to approach the evaluation phase in the eLearning production process
Conclusion
Looking for new ideas to streamline eLearning processes in 2016? Use the best practice advice in this article to implement a better process inside your organization. By setting up a process your team can follow, you can increase efficiency and productivity. This will assist you in delivering more eLearning in less time.
Keep reading: