eLearning Production Guidelines Aim
The broad aim of developing eLearning production guidelines for our organization was to provide clarity and direction, and in particular to:
- Establish standards that would deliver a recognizable brand, and a consistent experience for learners.
- Document compulsory components of our eLearning production process.
- Illustrate model elements of our eLearning design.
- Ensure that eLearning modules met with firm standards for design, language use, and reflected other internal policies.
- Identify and document working knowledge, e.g. technical requirements, industry design standards, and internal contacts.
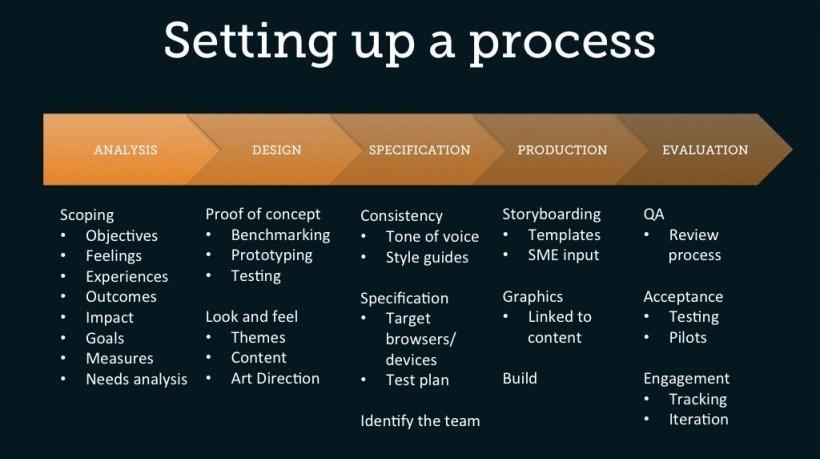
Approach
Before developing our eLearning production guidelines, a prototype eLearning module was created and tested with a select user group. We used a production team review, and the feedback from the module testers, to identify the broad principles that would guide the development of our production standards.
The next step in the development process was to review our eLearning creation software (Articulate Storyline), and evaluate the suitability of its design features and interaction functionality. We focused on including elements from Articulate Storyline that would meet with our broad development principles, that suited the firm’s learning environment, and which would lead to efficient, high quality output.
This approach was supplemented by a review of eLearning modules external to the firm to identify techniques and standards we would need to include in the guidelines. We found MOOCs particularly useful for this purpose, as well as a range of other free eLearning content. In addition, we reviewed what eLearning colleagues outside the firm had learned about module design, and for this element eLearning Industry was invaluable.
We also reviewed the firm’s resources, standards and policies that we would need to incorporate into our guidelines:
- The firm’s visual design guide which directed font and color palette choices.
- Image libraries created by the firm’s design and marketing departments, and used widely in marketing and communications material.
- The firm’s guide to plain English, which sets out communication styles.
- The firm’s diversity policy, which provided guidance on the use of characters.
- Our team’s existing guide to creating training content.
In addition to reviewing the firm’s resources and documented standards, we also consulted with the firm’s design experts and sought their input about the stylistic approach that we planned for our modules.
Once we completed our information gathering and research, the production guidelines were created in detail.
Key elements of eLearning production guidelines
The eLearning production guidelines required by an organization will be dependent upon a variety of factors particular to that organization. However, we would recommend that guidelines should include these elements.
Production team model
A detailed eLearning production model that fits with the organization’s resources and requirements, and that clearly sets out the roles of content experts, and the design and production teams is critical. An adjunct to this would be to establish baseline competencies for each of the design and production roles.
Module planning sequence
Although working with a relatively new technology, traditional techniques of training content development are still important. ELearning modules should commence development with clear learning objectives, and the learning objectives should be supported by a session plan and storyboard. Our guidelines provided a model for these elements.
Design elements
Design elements should be set out by model master slides. These can include standard slides for learning objectives, module instructions, feedback, and next steps for learners.
Other design elements to include:
- The font styles that will be used in the module, including text sizes for headings and body text.
- Preferred color palette, along with guidance on its use within the module, e.g. how it applies to text, headings, etc.
- Requirements for module navigation, and the extent to which the skin, or other navigation functionality will be applied.
Quality assurance and testing
It is necessary to develop review and testing processes that deliver constructive feedback on technical performance and content quality. The production guidelines should:
- Outline the required editing and proof reading processes.
- Detail testing requirements, e.g. if testing in multiple locations is required, and target groups for testing.
- Develop a model for feedback collection that includes a process, and a standard feedback form.
References to your organization’s standards
Relevant organization policies should be referenced in the guidelines. These might include the organization’s approach to language use, use of images and audio, copyright responsibilities, and diversity policies.
Networks and resources
Guidelines should provide a list of key internal contacts including design and technical experts, organizational learning and development teams, and language use and subject matter experts. External resources could also be added such as software specific documentation and discussion boards, and professional eLearning organizations and communities.
Conclusion
Why take the time to create eLearning production guidelines?
The development of our guidelines provided the opportunity to identify and clarify eLearning production standards, and to establish a basis for the continued enhancement of eLearning production.
Our focus was to support eLearning production by developing processes and standards that assured quality, and a recognizable brand and experience.
Our guidelines must be flexible, and will be regularly reviewed and revised. They will need to adapt to technological changes, and to changing organization requirements and expectations, and through this evolution continue to uphold core standards for eLearning production.