Engagement Automation And Triggers For Personalized Learning: Starting With Microlearning Engagement
Let’s begin with a few words about the basic concept behind microlearning engagement platforms. Microlearning engagement platforms are about delivering bite-sized learning to learners, whether in-class, for self-paced learning, repetitive practice, or performance support. In all cases, the system facilitates learning that is several minutes long – from several microlearning items in a classroom environment to perhaps one brief engagement daily (for learning repetition). Since we're serving small bites of learning, the trick is to serve the right learning at the right time, and to do so in a way that will keep the learner engaged.
If you’re a critical reader, you’ll have one question after reading the last paragraph: “How can you identify the right learning or the right time?” And it’s a great question, because doing that isn’t trivial. It requires the learning engagement system to be able to “sense” what’s going on in other systems. For instance, the system needs to “know” that a Sales person doesn’t know how to sell a certain product, or that a service technician isn’t familiar with a certain process. Often, this data isn’t available in any form in learning systems. That’s why engagement automation uses data from multiple external platforms to prompt learning, such as performance data.
Here’s an example: Performance data coming from the CRM tracks sales of products A, B, and C for each salesperson. Travis, a salesperson, doesn’t seem to be selling product C. Is he lacking in confidence? Suffering from a knowledge gap? Having other issues? Typically learning managers won’t even be aware of the issue, but if CRM data was used as an input to the learning delivery system, it would soon offer learning about product C, tailored to Travis' confidence level and actual knowledge. Other inputs can be that Travis wasn’t any good at assessments involving product C or seemed underconfident when questioned about it. These are also inputs to the learning delivery system.
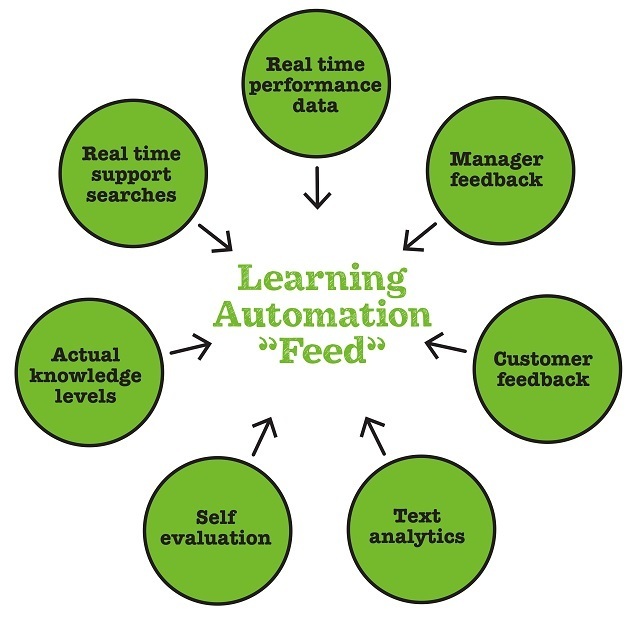
The multiple sources of data that the system "senses" to drive personalized learning.
Applying eLearning Engagement Automation
Now that we understand how engagement automation can be used, let’s investigate the process behind eLearning engagement automation:
- Learners are segmented into audiences (e.g. based on role, tenure, success rates, etc.).
- Learning items are classified and tagged (e.g. based on topic or complexity, imagine a bank of 300 questions, tagged by subject).
- Triggers and activities are defined (e.g. if a learner is in audience A enroll them into learning stream B).
- Feedback and engagement mechanisms are also implemented with triggers and actions (e.g. if learner X has a knowledge gap, apply more learning, or send a certain notification with feedback and a call to action to engage the learner).
- The process is measured and optimized.
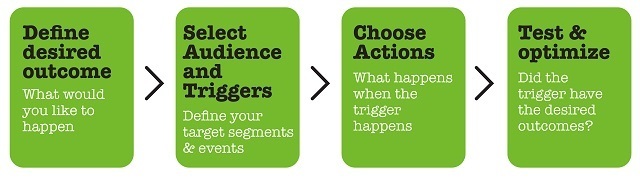
The engagement automation process.
Let's examine the process in more detail:
1. Segmenting Learner Audiences
Imagine you're a private tutor. To get the most from your tutoring sessions you would observe your student's results and ask questions to adapt learning to their needs. You will repeat points your student didn't fully understand, you will ask for feedback to gauge sentiment, and you will adapt exercises to the student's level of understanding.
When working with a larger group of learners, you would essentially do the same thing. Here, as you will not have the capacity to adapt to each learner personally, you will ask questions and observe behaviors to segment students into groups and deliver personalized learning. This is where learner audience segmentation comes into play.
Initial segmentation can be as follows:
Are they novices or veteran employees? (From HR – What is the employee's tenure in their role) What is their performance level?
- What position are they in? (From HR – employee role and position)
- What will they need the training for? (Role definitions)
- By when must their training be completed? (Role Requirements)
- What previous training have they had? (From the LMS – Previous courses taken)
Additionally, audience segmentation takes the following into account:
- How did learners perform so far? (From the LMS)
- What is their stance on training? Are they engaged? (From the LMS – How often users log in, what feedback are they leaving, etc.)
- How confident are they in their knowledge?
- What knowledge do they possess?
After a learning campaign is completed, you could ask more questions to see what further learning is necessary:
- Are learners applying what they've learned on the job? Are they making errors? (From enterprise systems – e.g. are calls logged correctly in the CRM)
- Are learners who completed training applying it to work? (e.g. are they selling the new product they were trained on?)
2. Triggers
Based on the information you collected you can now set triggers to automate actions. For instance, for learners that are knowledgeable but under confident, you can send feedback and badges telling them their knowledge is correct and that they have high scores. Over confident employees can get messages directing them to correct misconceptions. Triggers use guided adaptation, first defined by Bersin: Provide employees with data, knowledge, and guidance needed to continuously improve performance.
When a learner achieves a certain performance milestone (or misses it) actions can be additional learning, suggesting a course of action or manager-prompted feedback. In general, actions triggered belong to the following groups:
- Delivery and Enrollment: The right microlearning threads for the specific employee.
- Personalization: Delivery of personalized learning.
- Engagement: Encouraging and nudging relevant learners to participate in learning activities.
- Performance Support: Delivering training on the job to help employees improve their work.
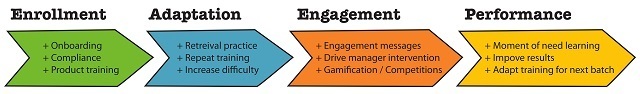
Delivery And Enrollment
Based on the standard training requirements for different employee segments (e.g. new hires, team managers, etc.), you can set automated triggers that add employees automatically to relevant courses or learning streams.
A relevant trigger for compliance can be set to review which employees completed certification training within the past 12 months. In addition to enrolling employees, the system should be able to trigger sending notifications to relevant employees and managers letting them know new learning materials are available and providing the time frame by which this training must be completed.
Personalizing Learning Delivery
SATs exams employ adaptive assessments – test difficulty increases based on the learner's success. There is no wizardry behind this and the mechanism is quite simple. Questions on each topic are pooled based on difficulty and once a learner answers enough questions from one pool correctly, the next batch of questions is automatically drawn from the next pool. The same simple process can be applied to create adaptive corporate training.
These mechanisms can also be used for spaced repetition – identifying weak and strong areas and applying spaced repetition accordingly.
Engagement
To drive high completion rates and make sure learners are attentive and earnest in their learning activities you can use engagement messages.
Imagine our learning system measures how many times each week a certain employee has engaged with their training materials. We could send feedback automatically such as messages acknowledging a certain learner's achievement in completing a learning campaign.
Learning engagement sometimes requires the support of direct managers. Here triggers can help us empower managers to take an active part in their report's training. We could, for instance, trigger notifications to the department manager that a certain employee is falling behind in his regulatory compliance training.
Triggering As A Form Of Performance Support
For organizations that are willing to take the extra step and seek a holistic learning experience, advanced learning systems can integrate with and draw real time data from enterprise systems such as CRMs, calendars, project management systems, and more. This will enable providing an extra layer of training triggered to provide performance support exactly at the moment of need.
Imagine for example triggering a 5-minute refresher session on a new company product automatically when a sales agent is scheduled to hold a meeting with a relevant prospective client. Alternatively, imagine employees who have recently had repeated reported safety incidents are automatically enrolled into a preventive safety training program.
If you want to know more about how learning engagement automation works, download the free eBook Next Generation Learning Delivery – Using Engagement Automation & Triggers For Personalized Learning today.








