From corporate training to small business exercises to education platforms, eLearning has taken the learning world by storm. It is the inexpensive, convenient replacement to traditional teaching methods. In an attempt to maximize this demand for efficient training, there has been a shift in focus for many organizations from traditional instructional design and development to rapid eLearning development. Although there is speculation over the effectiveness of rapid eLearning development, it is clear that in the right instances, completed correctly, it can actually add value to eLearning projects. When compared to traditional eLearning development, rapid development maintains more direct input from subject matter experts, allows for a faster turnaround, and can be created with a cheaper budget.
3 Important Reasons To Choose Rapid eLearning Development vs Traditional eLearning Development
- Subject Matter Expert Input
In traditional eLearning development, the material is passed from the Subject Matter Expert (SME) to the Instructional Designer (ID), so that the ID may use the material to design storyboards that represent how to effectively present the material to learners. The storyboards are then passed to an eLearning developer, who writes the coding to create the training program. While this does ensure that the material has pedagogical value, it also takes the material two steps away from the SME. Since the ID and eLearning developer don’t necessarily have any knowledge or experience with the content, maximizing the SME’s involvement in the process can be very beneficial to ensuring that the material is accurate. In rapid eLearning development, the SME may directly design and/or develop the material, with guidance by the ID. In this process, the ID serves as an advisor by coaching in the SME in defining objectives, advising them on delivery options, suggesting interactions, and validating training results (Boulet, 2012). Therefore, the pedagogy is preserved while the SME maintains direct input and involvement.Thanks to recent evolutions of eLearning content authoring tools, which focus on rapid eLearning development, SMEs are able to create eLearning content without programming skills. As long as the eLearning tool is easy to use, software savvy, produces flash files, has customizable templates, facilitates collaborative environments if needed, and allows for quiz incorporation (West, 2007), the SME should be able to input his or her content directly into the program without hardly any training. Rapid eLearning development tools such as Lectora, Captivate, Tool Book, Smart Builder, Storyline, and Zebra Zapps allow developers to create realistic interactions, multi-part decision making, randomized events, customized feedback, and learner-preference customizations without having any coding or programming knowledge (Unrein, 2012). This way, the SME may focus on the quality and content of the material instead of an eLearning developer focusing on the coding (Kursham, 2010). The integrity of the material is hereby preserved through development. - Faster Turnaround
One of the greatest draws to rapid eLearning development is the faster turnaround time of the training product. Traditional training can take months to complete as it goes from the SME, to the ID, to the eLearning developer, to a QA team, and back to the ID and/or developer possible multiple times, before being approved and launched. This process can take anywhere from 220-2,500 man hours to complete, requiring upwards of 4 developers to create the material within months (Rosen, 2006). This lengthy cycle looks something like this: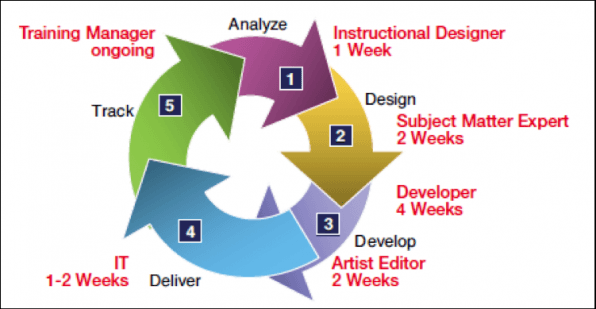
(West, 2007, p.2)Although it is an effective method for creating training materials, there is a high demand for speed to market for many of the companies requesting eLearning development. In fact, a 2004 Study by Bersin (2005, as cited by West, 2007), revealed that 89% of companies needed to develop part of the eLearning solution within 3 weeks of deciding to take their training online. As you can see from the chart above, this isn’t a realistic goal for the traditional eLearning development process. It is, however, realistic for the rapid eLearning development process, which looks more like this: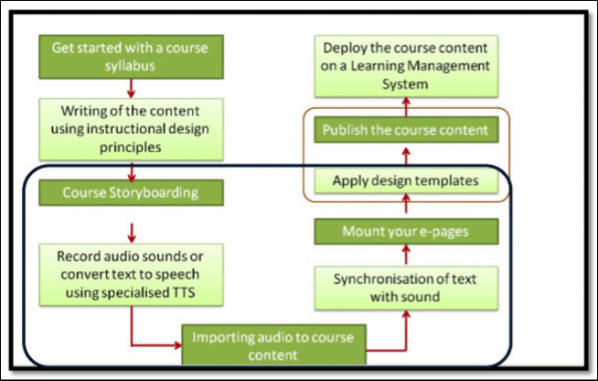
(Santally et. al, 2013, p.6)This process can be completed within 3 weeks, since there is less time spend on developing intricate coding both initially and for any possible adjustments required, thanks to the rapid eLearning content authoring tools. A great Instructional Designer or the SME without programming skills can directly create the material using these programs without wasting those precious man hours, thereby getting the content created and launched in an extremely timely manner, which is exactly what the market demands. - Cheaper Budget
Ultimately, the goal of any organization is to maximize profit; rapid eLearning development capitalizes on this goal. By reducing the time required to develop the eLearning project and not having to hire an expensive programmer with coding skills, rapid eLearning development allows the product to be completed on a cheaper budget than a traditionally developed product. According to West (2007), a traditionally developed eLearning course can take anywhere from $5,000-50,000 per hour of learning to create. Let’s be realistic: most small companies and education platforms don’t have that kind of budget. Even larger corporations with more finances in the pot may not want to spend that kind of money on eLearning, as it could have a short shelf life or could be a small example of a future, larger training course. Whatever the case may be, it is clear that the biggest draw and value to rapid eLearning development is the money that it will save the organization to develop their training.Implement Rapid eLearning Development with the Best Authoring Tool!Discover, choose and compare the top eLearning Authoring Tools Providers!
Thanks to the Subject Matter Expert’s direct input, the faster turnaround time, and the cheaper budget, rapid eLearning development has gained a lot of attention over the past several years. When completed correctly, rapid eLearning development takes into account both quality and quantity of the training created, thereby maximizing efficiency. This process has therefore added a great value to organizations seeking online training.
References:
Boulet, G. (2012). Rapid eLearning: Building a house without an architect. http://elearnmag.acm.org/archive.cfm?aid=2135884.
Kursham, M. (2010). Rapid eLearning. http://elinnovations.blogspot.com/2010/02/rapid-elearning.html
Rosen, A. (2006). Rapid eLearning: Another view on a thing fast. http://www.learningsolutionsmag.com/articles/217/rapid-e-learning-another-view-on-all-things-fast.
Santally, M.I., Rajabalee, Y., Cooshna-Nalk, D. (2012). Learning design implementation for distance e-Learning: Blending rapid e-Learning techniques with activity-based pedagogies to design and implement a socio-constructivist environment. http://www.eric.ed.gov/PDFS/EJ982978.pdf.
Unrein, J. (2012). Rapid power tools: The top performers of eLearning authoring software. http://elearnmag.acm.org/featured.cfm?aid=2221186.
West, E. (2007). Rapid e-Learning: Maturing technology brings balance and possibilities. http://i.i.com.com/cnwk.1d/html/itp/Adobe-Nielsen_RapideLearning.pdf








