Distributed Learning: A Flexible Learning Model For A Global Economy
As a general statement, "distributed learning" is learning that includes one or more of the following:
- Blended learning
Learning that combines instructor-led training (ILT) with Web-based training (WBT) and other learning activities outside the classroom (such as pre-work or on-the-job mentoring). - Mobile learning
Learning that occurs on a portable device, such as a tablet or smartphone. - Informal learning
Learning that occurs outside a formal learning environment (classroom, online class, etc.). This type of learning is facilitated by social interaction.
In the technical white paper Distributed Learning: A flexible learning model for a global economy, Obsidian Learning presents the distributed learning model they have used with great success for their clients.
Background
The design of effective, engaging learning should be supported by an understanding of how learning occurs (particularly for the adult learner) as well as knowledge of the technologies that best support learning.
Since 1998, Obsidian Learning has been providing medium and Fortune 500 firms with interactive learning programs grounded in cognitive research, adult learning theory, and universal design principles.
In 2015, Obsidian applied these practices to the design and development of Obsidian Black, an HTML5 authoring tool for today’s mobile learner. Their team of programmers and instructional designers collaborated to create a tool for rapid authoring of interactive content in native HTML5 for responsive output on all devices. Standards-conformant (SCORM/xAPI) content can be quickly exported for LMS/LRS integration and deployment.
About the Distributed Learning White Paper
The Distributed Learning: A flexible learning model for a global economy white paper discusses distributed learning as a method of engaging learners in a blended environment. In this paper, Obsidian reviews the literature on learning theories, in particular social theories of learning; describes the Obsidian Learning model of distributed learning; and presents case studies of Obsidian’s Distributed Learning model in practice.
The paper also discusses some of Obsidian’s core beliefs about learning, particularly in the digital age:
- First and foremost, learning must be fully learner-centered, supporting the learner not only in periods of formal training but also in times of need in the workplace. Instead of “death by PowerPoint” from the “sage on the stage,” learning should involve social, collaborative experiences as well as access to online tools.
- Second, learning should be blended. Particularly in times of economic downturn, learning experiences must be focused, easily manageable, and targeted to the unique needs of the adult learner. It is expensive, time-consuming, and ineffective to keep learners in a classroom for days. Instead, learning should be ongoing, occur when needed, and make use of inexpensive technologies.
- Third, learning should be a social experience. It should provide opportunities for collaboration and interaction – both within formal learning experiences and continuing in the workplace, in the form of collaborative problem-solving, ongoing performance support, and communities of practice.
About Obsidian’s Distributed Learning Model
Obsidian Learning uses the term "distributed learning" to describe learning that is:
- blended, using various combinations of ILT, WBT, and mobile learning
- spread out over time, including formal training, informal learning, refresher
- just-in-time (JIT) learning that occurs at the point of need, along with performance support
- focused on competency development rather than on general knowledge growth
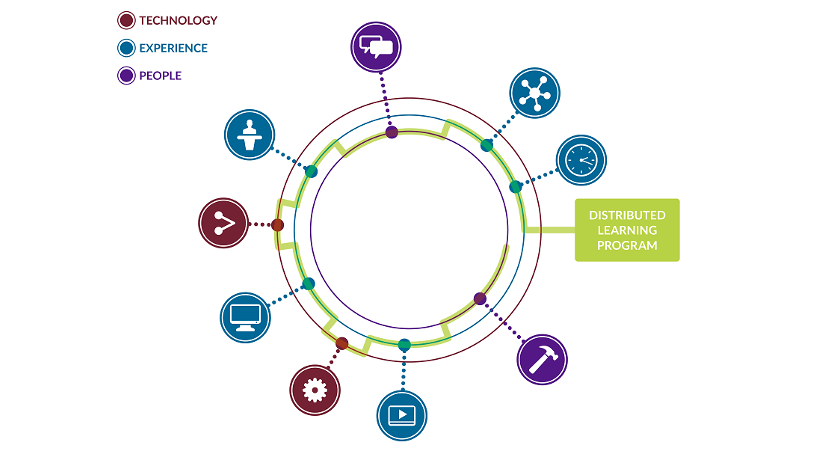
There are three major components of Obsidian’s Distributed Learning model.
- Technology
Through technology – in the classroom, on the LMS/LRS, on social media platforms like Twitter or Facebook – learners are empowered to collaborate with each other and to seek resources for their own personal learning networks (PLNs). - Experience
A variety of learning experiences using a variety of media – instructor-led training (both classroom and virtual), Web-based training, performance support tools (for just-in-time learning), communities of practice – leads to increased learner engagement and builds the technology-mediated collaboration skills that are so vital in our global economy. - People
Collaborative learning is a key component of Obsidian’s Distributed Learning model. Learning experiences should encourage collaborative problem-solving, learning through interaction with others, the development of ongoing communities of practice, and forming connections.
Case Studies
Obsidian’s Distributed Learning model is not only a valuable tool for the design of distributed learning environments, it can also provide significant savings for your organization or clients. The white paper presents two case studies demonstrating how Obsidian’s distributed learning solutions have improved learning effectiveness and saved their clients millions of dollars.
Who Can Benefit from This Paper
This white paper will inform you about some of the foundational research on learning and ways in which it can be applied to the design of powerful learning solutions. The paper will be of interest to various professionals involved in the creation or delivery of online training, including:
- Training Managers
- Instructional Designers
- Learning Strategists
- Graphic Designers
- Project Managers
- Account Managers
Download this free white paper to learn more about Obsidian’s Distributed Learning model.